![]()
Part VII: William Tyndale- The Father of the English Bible
By the start of the sixteenth century, 116 years had passed since Wycliffe’s translation, and great changes had taken place across Europe. England had begun to arise from both culturally and politically with the end of numerous internal wars. The Tudors, especially Henry VIII, had made England a world power. Powerful forces were at work pulling the world out of the Dark Ages as the light of God’s Word began to shine.
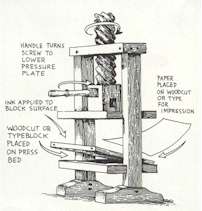 First, the invention of the printing press in 1450
A.D. and moveable type in 1455 made the spreading of the printed Bible possible. Also,
with the rise of a merchant class in England, more and more of the middle class were
educated to read. The fall of Constantinople in 1453 to the Turks unlocked thousands of
Greek and Latin manuscripts previously unknown. As the scholars fled from the Turks with
their manuscripts in hand they sparked a "renaissance" of new interest in Greek
and Latin all over Europe. Ultimately this caused a professor at the University of Paris
to prepare a printed text of the New Testament using several Greek manuscripts. The result
is the Erasmus Greek New Testament, 1516 A.D., which was used to prepare the first English
translation of the Bible directly from the Greek.
First, the invention of the printing press in 1450
A.D. and moveable type in 1455 made the spreading of the printed Bible possible. Also,
with the rise of a merchant class in England, more and more of the middle class were
educated to read. The fall of Constantinople in 1453 to the Turks unlocked thousands of
Greek and Latin manuscripts previously unknown. As the scholars fled from the Turks with
their manuscripts in hand they sparked a "renaissance" of new interest in Greek
and Latin all over Europe. Ultimately this caused a professor at the University of Paris
to prepare a printed text of the New Testament using several Greek manuscripts. The result
is the Erasmus Greek New Testament, 1516 A.D., which was used to prepare the first English
translation of the Bible directly from the Greek.
 During
the same time period, things were stirring in Germany as well. In 1517, Martin
Luther nailed his Ninety-five Theses on the door of the Wittenburg church, attacking
numerous Church doctrines and practices. Luther, a professor of Theology at the
University of Wittenburg, also wrote many other works. He is most greatly known for
denouncing teaching that said salvation could be earned by works, teaching instead what
the Bible says: that salvation is by faith alone, apart from works (Romans 3:28).
Certain clergy in the Church were taking advantage of the common man's ingorance of the
Scriptures, since there were no Bibles in the vernacular, and teaching that one must
purchase indulgences to obtain salvation, or to free one's loved one from purgatory into
heaven. Thus, these clergymen got rich off of the ignorance and blind faith of the
people. Martin Luther, and many others, were appalled. Luther's boldest act
sought to destroy the clergy's abuse of power: the translation of the Bible into German.
He was not the first to translate the Bible into German, but he was the first to
make a thorough, scholarly study of the Latin, Greek, and Hebrew text and translate them
into the German language spoken on the streets by everyday Germans. He said,
"We must not...ask the Latin letters how we are to speak German, but we must ask the
mother in the home, the children on the street, the common man in the marketplace about
this, and look them in the mouth to see how they speak, and afterwards do our
translating." Luther was excommunciated and banned by the Roman Church for his
teachings, but during his lifetime an estimated 100,000 copies of his German New Testament
were distributed. The light of God's Word shining in Germany would later be termed
by historians as the start of the "Reformation."
During
the same time period, things were stirring in Germany as well. In 1517, Martin
Luther nailed his Ninety-five Theses on the door of the Wittenburg church, attacking
numerous Church doctrines and practices. Luther, a professor of Theology at the
University of Wittenburg, also wrote many other works. He is most greatly known for
denouncing teaching that said salvation could be earned by works, teaching instead what
the Bible says: that salvation is by faith alone, apart from works (Romans 3:28).
Certain clergy in the Church were taking advantage of the common man's ingorance of the
Scriptures, since there were no Bibles in the vernacular, and teaching that one must
purchase indulgences to obtain salvation, or to free one's loved one from purgatory into
heaven. Thus, these clergymen got rich off of the ignorance and blind faith of the
people. Martin Luther, and many others, were appalled. Luther's boldest act
sought to destroy the clergy's abuse of power: the translation of the Bible into German.
He was not the first to translate the Bible into German, but he was the first to
make a thorough, scholarly study of the Latin, Greek, and Hebrew text and translate them
into the German language spoken on the streets by everyday Germans. He said,
"We must not...ask the Latin letters how we are to speak German, but we must ask the
mother in the home, the children on the street, the common man in the marketplace about
this, and look them in the mouth to see how they speak, and afterwards do our
translating." Luther was excommunciated and banned by the Roman Church for his
teachings, but during his lifetime an estimated 100,000 copies of his German New Testament
were distributed. The light of God's Word shining in Germany would later be termed
by historians as the start of the "Reformation."
 Onto this stage of God-appointed drama walked a man of humble birth
but superior education – William Tyndale. Born in Gloucestershire, England in the
early 1490s and educated at Oxford and Cambridge (where he studied under Erasmus), Tyndale
was so fluent in 7 languages that you could not tell which was his native tongue. Like
other men of his time, he began to question the abuses and corruption of the Church. God
lit a fire in Tyndale’s heart to provide God’s Word in the language of the
people of England. While working as a tutor, Tyndale responded to a Bishop’s
challenge that "we would be better without God’s law than (without) the
Pope’s" by retorting, "I defy the Pope and all his laws; of God
spares my life ere many years I will cause a boy that driveth the plough shall know more
of the Scripture than thou doest." Tyndale left his tutoring position and
traveled to London to gain permission to translate the Bible from the Bishop of London. To
help stamp out the influence of the Wycliffe’s Lollards, a law had been passed in
1408 making it punishable by death to translate the Bible into English, and the Bishop was
unwilling to change this law. It soon became apparent that no place in England was safe
for Tyndale to translate the Bible, so he left England- never to return.
Onto this stage of God-appointed drama walked a man of humble birth
but superior education – William Tyndale. Born in Gloucestershire, England in the
early 1490s and educated at Oxford and Cambridge (where he studied under Erasmus), Tyndale
was so fluent in 7 languages that you could not tell which was his native tongue. Like
other men of his time, he began to question the abuses and corruption of the Church. God
lit a fire in Tyndale’s heart to provide God’s Word in the language of the
people of England. While working as a tutor, Tyndale responded to a Bishop’s
challenge that "we would be better without God’s law than (without) the
Pope’s" by retorting, "I defy the Pope and all his laws; of God
spares my life ere many years I will cause a boy that driveth the plough shall know more
of the Scripture than thou doest." Tyndale left his tutoring position and
traveled to London to gain permission to translate the Bible from the Bishop of London. To
help stamp out the influence of the Wycliffe’s Lollards, a law had been passed in
1408 making it punishable by death to translate the Bible into English, and the Bishop was
unwilling to change this law. It soon became apparent that no place in England was safe
for Tyndale to translate the Bible, so he left England- never to return.
 With a price on
his head, he traveled under disguise and secrecy throughout Germany as he completed his
translating work. He visited with Luther and, although they firmly agreed on Sola
Scriptura ("Scripture alone" for guidance in Christian faith), they did not
agree on other doctrines, and so they each traveled their own paths. Tyndale completed the
New Testament in late 1525 and began the dangerous task of smuggling them into England in
every possible way. Providentially, the docks of London were in the hands of many Germans
friendly to the Reformation and the New Testaments soon reached the eager hands of the
English people. They also aroused the anger of the clergy. Now the common people could
read the truth of God’s Word for themselves. What had begun as a small spark with
John Wycliffe had become a blazing fire that reached even into the king’s bedroom!
Anne Boleyn, King Henry VIII’s wife, not only had a copy of Tyndale’s Obedience
of the Christian Man, which she gave to as a gift to the King, as well as her own copy
of Tyndale’s 1534 New Testament. Although outwardly he opposed the
"reformation," it suited Henry VIII to use it to obtain his divorce from his
Catholic wife (so that he could marry Anne), remove the Pope as head of the Church, and
claim that title (as well as the wealth) for himself. Yet the King continued to oppose
Tyndale and his Bibles, and Tyndale had to continue smuggling his Bibles into England
illegally.
With a price on
his head, he traveled under disguise and secrecy throughout Germany as he completed his
translating work. He visited with Luther and, although they firmly agreed on Sola
Scriptura ("Scripture alone" for guidance in Christian faith), they did not
agree on other doctrines, and so they each traveled their own paths. Tyndale completed the
New Testament in late 1525 and began the dangerous task of smuggling them into England in
every possible way. Providentially, the docks of London were in the hands of many Germans
friendly to the Reformation and the New Testaments soon reached the eager hands of the
English people. They also aroused the anger of the clergy. Now the common people could
read the truth of God’s Word for themselves. What had begun as a small spark with
John Wycliffe had become a blazing fire that reached even into the king’s bedroom!
Anne Boleyn, King Henry VIII’s wife, not only had a copy of Tyndale’s Obedience
of the Christian Man, which she gave to as a gift to the King, as well as her own copy
of Tyndale’s 1534 New Testament. Although outwardly he opposed the
"reformation," it suited Henry VIII to use it to obtain his divorce from his
Catholic wife (so that he could marry Anne), remove the Pope as head of the Church, and
claim that title (as well as the wealth) for himself. Yet the King continued to oppose
Tyndale and his Bibles, and Tyndale had to continue smuggling his Bibles into England
illegally.
 Tyndale was constantly revising his work on the New Testament
(with his 1534 edition considered his finest) while translating the Old Testament as well.
In 1530, he completed the Pentateuch; in 1531, the book of Jonah. He did all of this work
while in hiding, constantly evading the host of spies and bounty hunters sent by Rome and
Henry VIII to find and kill him. Finally, he was betrayed by a friend, imprisoned in
Vilvorde Castle, and tried for heresy by Rome. After 18 months of imprisonment he was
strangled and then burned at the stake on Oct.6, 1536 A.D. Granted a final word, William
Tyndale prayed "Lord, open the King of England’s eyes." This famous
prayer would soon be answered when the King had a change in heart. In 1537, King Henry
VIII granted his approval for an English Bible, the second edition of the Coverdale Bible,
to be distributed throughout England. Little did Henry know that over 70% of that Bible
was Tyndale’s work- the very man he had put to death only one year before.
Tyndale was constantly revising his work on the New Testament
(with his 1534 edition considered his finest) while translating the Old Testament as well.
In 1530, he completed the Pentateuch; in 1531, the book of Jonah. He did all of this work
while in hiding, constantly evading the host of spies and bounty hunters sent by Rome and
Henry VIII to find and kill him. Finally, he was betrayed by a friend, imprisoned in
Vilvorde Castle, and tried for heresy by Rome. After 18 months of imprisonment he was
strangled and then burned at the stake on Oct.6, 1536 A.D. Granted a final word, William
Tyndale prayed "Lord, open the King of England’s eyes." This famous
prayer would soon be answered when the King had a change in heart. In 1537, King Henry
VIII granted his approval for an English Bible, the second edition of the Coverdale Bible,
to be distributed throughout England. Little did Henry know that over 70% of that Bible
was Tyndale’s work- the very man he had put to death only one year before.
We owe much to William Tyndale. He set his face to the task of giving the Bible to the common man in a language he could understand and he never looked back. He translated alone without the comfort of friends or family and paid with his life, never knowing the impact he and his work would have on the world. Tyndale’s translations were of good quality as well: more than 90% of his wordings appear in the King James Version published almost 100 years later and 75% of his wordings appear in the Revised Standard Version of 1952. He is rightfully called the Father of the English
Copyright © 1998-2002, The Ancient Page